Parts of a Plastic Molding Machine: An In-Depth Guide
Plastic molding machines, also known as injection molding machines, are critical in manufacturing a wide range of plastic products. Understanding the components of these machines is essential for operators, technicians, and anyone involved in the plastic manufacturing industry. This article delves into the various parts of plastic molding machine, explaining their functions and importance.
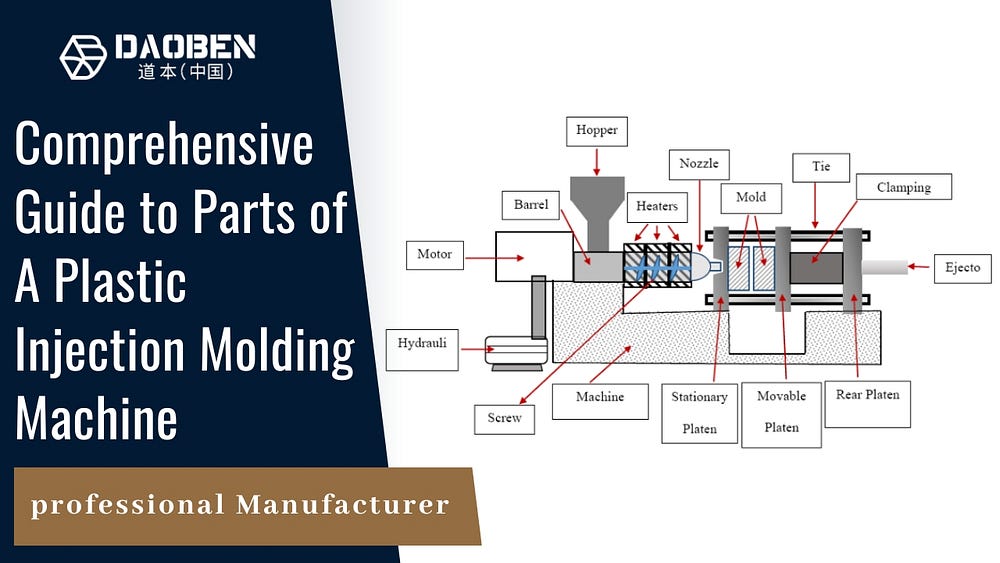
1. Hopper
The hopper is the entry point for raw plastic material, usually in the form of granules or pellets. This component feeds the plastic into the machine’s barrel and is often equipped with a dryer to remove any moisture from the material, ensuring high-quality output.
Key Features:
- Material Loading: Holds and supplies the raw plastic.
- Drying Capability: Removes moisture from plastic pellets.
- Capacity: Varies based on machine size and production requirements.
2. Barrel and Screw Assembly
The barrel and screw assembly is where the raw plastic material is melted, mixed, and pushed forward into the mold. The screw rotates within the barrel, generating heat through friction and external heaters to melt the plastic.
Key Features:
- Heating Zones: Multiple heaters maintain the required temperature.
- Screw Designs: Varies in diameter and pitch for different materials and products.
- Mixing and Melting: Ensures uniform plastic melt for consistent product quality.
3. Injection Unit
The injection unit is responsible for injecting the molten plastic into the mold. It consists of a hydraulic or electric motor that drives the screw forward, forcing the plastic through a nozzle into the mold cavity.
Key Features:
- Injection Pressure: Determines the force with which the plastic is injected.
- Speed Control: Regulates the injection speed for precision molding.
- Nozzle: Connects the barrel to the mold, ensuring smooth plastic flow.
4. Clamping Unit
The clamping unit holds the mold halves together during the injection and cooling processes. It provides the necessary force to keep the mold closed and can open the mold to eject the finished product.
Key Features:
- Clamping Force: Measured in tons, ensures the mold stays closed.
- Opening and Closing Mechanism: Hydraulically or mechanically driven.
- Mold Alignment: Ensures precise matching of mold halves for product accuracy.
5. Mold
The mold is a hollow metal block into which the molten plastic is injected to form the desired shape. Molds are custom-designed for specific products and are made from durable materials like steel or aluminum.
Key Features:
- Cavity and Core: Shapes the exterior and interior of the product.
- Cooling Channels: Circulate coolant to solidify the plastic quickly.
- Ejection System: Pushes the finished product out of the mold.
6. Ejector System
The ejector system removes the molded part from the mold once it has cooled and solidified. This system typically uses pins or plates that push the part out when the mold opens.
Key Features:
- Ejector Pins: Strategically placed to push the product out without damage.
- Ejector Plate: Moves the pins forward and back.
- Control Mechanism: Ensures synchronized ejection with mold opening.
7. Control Panel
The control panel is the brain of the plastic molding machine. It allows operators to set and monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, injection speed, and clamping force.
Key Features:
- User Interface: Touchscreens or buttons for easy operation.
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): Manages machine functions and processes.
- Data Monitoring: Tracks machine performance and product quality.
8. Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system provides the necessary power to operate the injection and clamping units. It consists of pumps, valves, and cylinders that convert hydraulic energy into mechanical movement.
Key Features:
- Hydraulic Pumps: Generate the pressure needed for operation.
- Valves: Control the flow and direction of hydraulic fluid.
- Cylinders: Convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical force.
9. Cooling System
The cooling system is crucial for maintaining the moulding machine operating temperature and cooling the molded parts. It usually includes water or oil-based cooling channels within the mold and the machine.
Key Features:
- Cooling Channels: Circulate coolant to regulate temperature.
- Chiller Units: Maintain consistent coolant temperature.
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor and adjust cooling as needed.
10. Base and Frame
The base and frame provide the structural support for the entire molding machine. They must be sturdy and stable to handle the forces generated during the molding process.
Key Features:
- Durable Construction: Often made from high-strength steel.
- Vibration Dampening: Reduces operational vibrations for precision.
- Support Structures: Ensure stability and safety of the machine.
Conclusion
Understanding the parts of a plastic molding machine is essential for efficient operation and maintenance. Each component plays a critical role in the overall performance and quality of the molded products. By familiarizing yourself with these parts, you can better troubleshoot issues, perform routine maintenance, and ensure optimal machine performance for your plastic manufacturing needs.

Comments
Post a Comment